A heat exchanger is a crucial component of a furnace that transfers heat from the combustion chamber to the air that circulates throughout your home. A bad heat exchanger can cause a variety of issues, and some of the most common symptoms include:
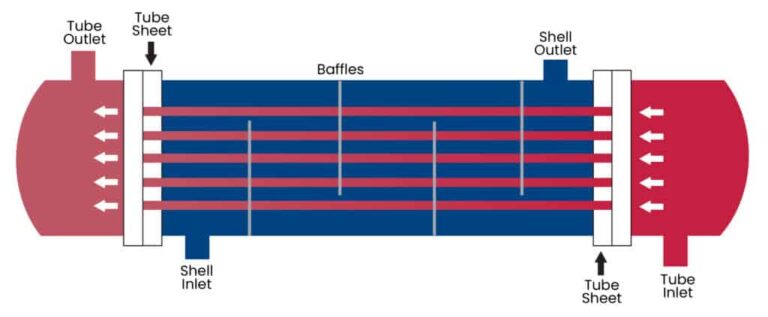
Signs of a Bad Heat Exchanger
- Carbon monoxide leaks: A cracked or damaged heat exchanger can lead to dangerous carbon monoxide leaks, which can cause headaches, dizziness, nausea, and even death.
- Uneven heating: If your furnace is producing heat, but it’s not evenly distributed throughout your home, it could be a sign of a bad heat exchanger.
- Strange noises: A damaged heat exchanger can cause strange noises like banging, popping, or rattling sounds coming from your furnace.
- Increased energy bills: A damaged heat exchanger can cause your furnace to work harder to heat your home, leading to increased energy bills.
- Poor air quality: A bad heat exchanger can lead to poor air quality due to the accumulation of dust and debris inside your furnace.
- Foul odors: A cracked heat exchanger can release unpleasant smells, like a burning odor, metallic smell, or musty odor.
- Visible cracks or damage: If you can see visible cracks or damage to your heat exchanger, it’s a clear sign that it needs to be repaired or replaced.
If you notice any of these symptoms, it’s essential to call a professional HVAC technician immediately to inspect your furnace and determine the cause of the issue.
A damaged heat exchanger is not something to ignore, as it can be dangerous to your health and safety.
Carbon monoxide (CO) is a poisonous gas that can be lethal in high concentrations. The acceptable levels of carbon monoxide in the air depend on the duration of exposure. Here are the recommended levels of CO exposure:
- Occupational exposure: The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) sets the permissible exposure limit (PEL) for CO at 50 parts per million (ppm) over an 8-hour workday.
- Residential exposure: The US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) recommends a limit of 9 ppm for continuous exposure over an 8-hour period, and a limit of 35 ppm for exposure over a 1-hour period.
It’s important to note that even low levels of carbon monoxide exposure can cause symptoms like headaches, dizziness, nausea, and confusion, which can lead to serious health problems over time. In addition, carbon monoxide is a colorless and odorless gas, so it’s important to have carbon monoxide detectors installed in your home to alert you if levels are reaching dangerous levels. If you suspect that you have been exposed to high levels of carbon monoxide, it’s crucial to seek medical attention immediately.